Broadband Connectivity. Which is the best solution for you?
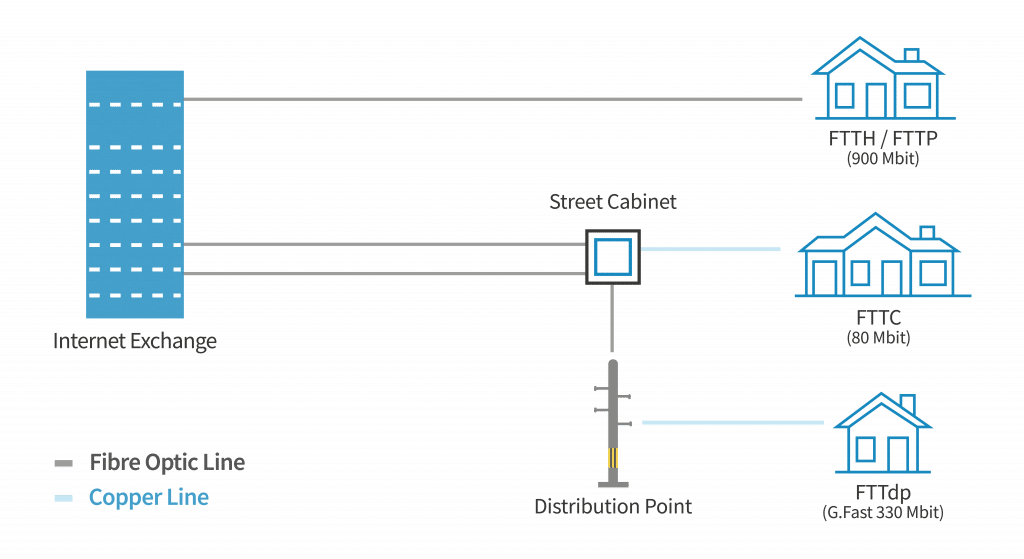
The landscape of broadband connectivity has evolved significantly over the years, bringing faster and more reliable internet options to both residential and commercial users. Three main types of broadband connections are prevalent in the UK: FTTC (Fibre to the Cabinet), FTTdp (Fibre to the Distribution Point), and FTTP (Fibre to the Premises). Each technology offers distinct advantages and caters to different needs and usage scenarios. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision about which broadband service best suits your requirements.
FTTC vs FTTPdp vs FTTP.
FTTC (Fibre to the Cabinet):
FTTC is the most widely used broadband technology in the UK. It involves running fibre optic cables from the local telephone exchange to a street cabinet (those green cabinets often seen on street corners). From the cabinet, traditional copper wiring is used to connect the fibre network to individual homes. This hybrid approach leverages the existing copper infrastructure, making it a cost-effective solution.
FTTdp (Fibre to the Distribution Point):
FTTdp, also known as G.Fast, is an enhanced version of FTTC. It extends the fibre network closer to homes, stopping at a distribution point (often a smaller box located nearer to the premises) instead of a street cabinet. This approach reduces the length of copper wiring needed, resulting in higher speeds and better performance.
FTTP (Fibre to the Premises):
FTTP, also known as FTTH (Fibre to the Home), represents the pinnacle of broadband technology, providing a direct fibre optic connection from the exchange to the user’s property. This eliminates the use of copper altogether, resulting in ultra-fast and highly reliable internet connectivity.
How do these types of connectivity work?
FTTC, a fibre optic connection between your local telephone exchange connected to the cabinet, and from this distribution point copper phone wiring is used to transfer data, just like traditional ADSL broadband.
With FTTdp the fibre runs to the street cabinet and is split into multiple fibre optic cables and carries on to a distribution point. This is situated much closer to the premises. The final connection is still made over copper cable but it is typically much shorter. This enables much higher internet speeds.
Advantages:
Affordability: It is Cost-effective as it uses existing phone wiring to provide internet connectivity.
Availability: FTTC is the most common internet connection for both commercial and domestic use. FTTdp is becoming available although Openreach has paused new installations in favor of FTTP
Disadvantages:
Lower Speed connectivity: Depending on the number of users sharing the connection, this may vary throughout the day. In addition, the further the property is from the cabinet the lower the broadband connectivity will be.
Maximum theoretical throughput is 80Mbits per second download and 20 uploads. Although in reality, the maximum you will achieve is 76 down 19 up. Most installations are however slower again.
FTTdp G.fast an even faster copper-based broadband. This delivers 330 Mbit/s download and 50 Mbit/s
It is quite affordable too and it is used to adjust speedhigher frequencies using special equipment fitted to the cabinet. You can increase the speed up to four times compared to the traditional Fibre to the cabinet connection.
On the other hand, FTTP broadband (fibre to the premises), also known as FTTH (fibre to the home) delivers data just with fibre optic cables unlike FTTC which still uses copper wiring. Hence, data speed is higher and distance from properties are longer. FTTP can deliver ultrafast speeds reaching up to 900Mb.
Both fibre connections are offered for domestic and commercial use but the cost may vary from one provider to another. FTTC used slower copper cables to distribute the connectivity whereas FTTP uses fibre cables which makes it faster and a bit more expensive.
FTTP is generally offered in multiple speed tiers from 150 right up to 900 Mbits
Choosing the Right Broadband Technology:
When deciding which broadband technology is right for you, consider your specific needs and what is available in your area. FTTC is suitable for most residential users who need reliable internet for everyday activities such as browsing, streaming, and working from home. FTTdp offers a middle ground with higher speeds and improved performance, making it a good choice for households with heavier internet usage. FTTP is the best option for those who require the highest speeds and most reliable connection, such as businesses or homes with multiple high-bandwidth devices.
Understanding the differences between FTTC, FTTdp, and FTTP is essential for making an informed decision about your broadband service. Each technology has its unique benefits and limitations, and the right choice depends on your usage requirements and the available infrastructure in your area. For personalized advice and assistance in choosing the best broadband solution, the Twisted Pair Technologies team is here to help you navigate the options and ensure you get the most out of your internet connection.