Faster Networks for FREE our Top 5 Tips
Whether your a seasoned network admin or have very little technical knowledge there will be simple changes you can make to improve your network. These are things we always check when we are looking for network faults.
1. Patch cords x2

Check for:
- Are of the correct type Cat5(e) / Cat6 / Cat6a and shielding
- Not damaged run over or otherwise abused.
- Check the cables are run free from kinks, sharp bends and tension.
- Check the cable is properly secured in the RJ45 Plug at each end with no wires exposed.
- Remember to check the cable from the computer to the port on the wall and the cable in the data cabinet to the switch.
Also checking if there any special requirement for shielding. Most copper networks are Unshielded Twisted Pair or UTP. However there are several Shielded Twisted Pair (SFP) cables.
Replacing these is easy, cheap and often wise in fault finding. This is especially important when cables. have been terminated by hand without moulded connections.
2. Wireless networks
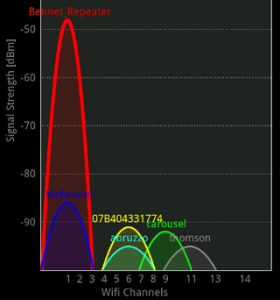
Most wifi networks are on the frequency 2.4 GHz and it’s really busy out there!
Check the channel your network is transmitting There are only 14 channels (frequencies) available and with most systems on the 2.4Ghz band using multiple channel, as can be seen in the graph, to enhance speed there are only 3 real channels.
Download a Wifi Analyser application for your phone this will allow you to optimise the channel you are using. The screen shot is from the android app wifi analyser.
There maybe overlaps which are free where as you might be using the most congested channel.
Check which standard your network is using. The most common types are 802.11b, 802.11g & 802.11n from oldest to newest and reflect maximum connection speeds of 11, 54 & 150 Megabits per second. Therefore make sure all of your equipment (wireless access points and network cards) are set to run at the fastest speed.
You could also check if your wireless is dual band and can work in the 5GHz band. If so check it is simultaneous dual band with the 2.4 GHz still running or you may lose lots of devices from the network. This is because separate aerials are required for the 5GHz spectrum and many devices only have 2.4 GHz aerials.
The newest standard 802.11ac wasn’t widely adopted at the time of writing. However see the article on 802.11ac here
3. Check your Server
Connections ensure your server is patched in to the correct port on the switch. Ideally this should be connected to your fastest or core switch if you have multiple switches. Check if your server has dual network ports. If so can this be patched to your switch for double the bandwidth if you have a suitable managed switch. Check carefully before you do this!
4. Pay careful attention to uplinks
Where a remote cabinet or local switch is uplinked to another, pay special attention as this is a bottle neck point and the effect any fault is multiplied. Check the switches at both ends and switch status lights.
If you have a layer 2 managed switch check the network administration (usually a web admin page) to check the port settings. Also if both switches support Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) and you have two uplink cables you can double the bandwidth across the bottleneck
Check for all the usual patch cord issues but pay special attention to making sure the links are the right length and cable type.
5. Check your Switches
We often see faults where extra data ports have been needed and small local, 5 or 8 port switch has been installed to cheaply add the extra capacity. These are often left under desks and kicked about. This combined with poor quality patch leads is almost certainly going to lead to problems.
Ideally add additional data points and switch capability in the nearest data cabinet and remove the rouge switch. This maintains network control to the end user port. Combined with Layer 2 managed switches gives powerful monitoring and control over network traffic and events.
Conclusion
As you can see there are many steps you can take to sort out and fix minor network issues in house. For fixed network fault finding we would recommend having your network tested to the relevant standards using a fluke or equivalent test equipment. Just ask if you want this service.
These are just a few small steps. If you have any questions about this please get in touch.
We also offer a Free Network report for local companies.